@PropertySource 注解提供了一种方便的声明性机制,用于将 PropertySource 添加到 Spring 容器的 Environment 环境中。该注解通常搭配 @Configuration 注解一起使用。本文将介绍如何使用 @PropertySource 注解,并通过分析源码解释外部配置文件是如何被解析进入 Spring 的 Environment 中。
使用方式
@Configuration 注解表示这是一个配置类,Spring 在处理配置类时,会解析并处理配置类上的 @PropertySource 注解,将对应的配置文件解析为 PropertySource,添加到 Spring 容器的 Environment 环境中。这样就可以在其他的 Bean 中,使用 @Value 注解使用这些配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/player.properties", encoding = "UTF-8")
public class PropertySourceConfig {
@Bean
public Player player() {
return new Player();
}
}
public class Player {
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Value("${player.nickname}")
private String nickname;
}
|
配置文件
测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class PropertySourceTest {
@Test
public void test() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PropertySourceConfig.class);
Player player = (Player) ac.getBean("player");
System.out.println(player);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = ac.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("player.nickname");
System.out.println(property);
ac.close();
}
}
|
测试结果
1
2
| Player{name='null', age=null, nickname='Tom'}
Tom
|
源码分析
关于 Spring 是如何处理配置类的请参见之前的文章:
获取 @PropertySource 注解属性
Spring 在解析配置类构建配置模型时,会对配置类上的 @PropertySource 注解进行处理。Spring 将获取所有的 @PropertySource 注解属性,并遍历进行处理。
@PropertySource 注解是可重复的,一个类上可以标注多个@PropertySources 注解包含 @PropertySource 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass)
throws IOException {
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.warn("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
}
|
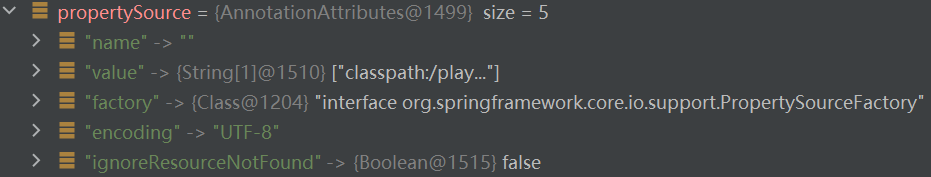
使用 IDEA 查看 AnnotationAttributes:
处理 @PropertySource 注解属性
- 读取
@PropertySource 注解属性的信息,如名称、编码和位置等等
- 遍历
location 查找资源
- 通过
PropertySourceFactory 使用资源创建属性源 PropertySource
- 将属性源添加到
Environment
注意属性源 PropertySource 不是 @PropertySource 注解,而是表示 name/value 属性对的源的抽象基类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| private void processPropertySource(AnnotationAttributes propertySource) throws IOException {
String name = propertySource.getString("name");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(name)) {
name = null;
}
String encoding = propertySource.getString("encoding");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(encoding)) {
encoding = null;
}
String[] locations = propertySource.getStringArray("value");
Assert.isTrue(locations.length > 0, "At least one @PropertySource(value) location is required");
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = propertySource.getBoolean("ignoreResourceNotFound");
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factoryClass = propertySource.getClass("factory");
PropertySourceFactory factory = (factoryClass == PropertySourceFactory.class ?
DEFAULT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_FACTORY : BeanUtils.instantiateClass(factoryClass));
for (String location : locations) {
try {
String resolvedLocation = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(resolvedLocation);
addPropertySource(factory.createPropertySource(name, new EncodedResource(resource, encoding)));
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
if (ignoreResourceNotFound) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Properties location [" + location + "] not resolvable: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (ignoreResourceNotFound &&
(ex instanceof FileNotFoundException || ex instanceof UnknownHostException)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Properties location [" + location + "] not resolvable: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
|
添加属性源到 Environment
将属性源添加到 Environment 中有以下几个规则:
- 所有通过
@PropertySource 注解加入的属性源,name 都会添加到 propertySourceNames
propertySourceNames 为空时,代表这是第一个通过 @PropertySource 注解加入的属性源,添加到最后(前面有系统属性源)propertySourceNames 不为空时,添加到上一个添加到 propertySourceNames 中的属性源的前面(后来居上)- 添加到
propertySources 的方法中都是先尝试移除,后添加(代表可能有顺序调整,具体场景不知)
- 如果已存在通过
@PropertySource 注解加入的属性源,则扩展为 CompositePropertySource,里面包含多个同名属性源(后来居上)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| private void addPropertySource(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
String name = propertySource.getName();
MutablePropertySources propertySources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) this.environment).getPropertySources();
if (propertySources.contains(name) && this.propertySourceNames.contains(name)) {
PropertySource<?> existing = propertySources.get(name);
PropertySource<?> newSource = (propertySource instanceof ResourcePropertySource ?
((ResourcePropertySource) propertySource).withResourceName() : propertySource);
if (existing instanceof CompositePropertySource) {
((CompositePropertySource) existing).addFirstPropertySource(newSource);
}
else {
if (existing instanceof ResourcePropertySource) {
existing = ((ResourcePropertySource) existing).withResourceName();
}
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(newSource);
composite.addPropertySource(existing);
propertySources.replace(name, composite);
}
}
else {
if (this.propertySourceNames.isEmpty()) {
propertySources.addLast(propertySource);
}
else {
String firstProcessed = this.propertySourceNames.get(this.propertySourceNames.size() - 1);
propertySources.addBefore(firstProcessed, propertySource);
}
}
this.propertySourceNames.add(name);
}
|
可以适当地将添加属性源和使用属性分开看待,Environment 是它们产生联系的枢纽,@PropertySource 注解的处理过程是 @Configuration 注解的处理过程的一部分,在文件中的配置转换成为 Environment 中的 PropertySource 后,如何使用它们是独立的一件事情。
关于搭配使用的 @Value 注解是如何工作的,可以参考文章: