Configuration 注解是 Spring 中常用的注解,在一般的应用场景中,它用于标识一个类作为配置类,搭配 Bean 注解将创建的 bean 交给 Spring 容器管理。神奇的是,被 Bean 注解标注的方法,只会被真正调用一次。这种方法调用被拦截的情况很容易让人联想到代理,如果你在 Debug 时注意过配置类的实例,你会发现配置类的 Class 名称中携带 EnhancerBySpringCGLIB。本文将从源码角度,分析 Configuration 注解是如何工作的。
测试用例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Configuration public class BeanConfig { @Bean public Person lisi () { return new Person ("lisi" , 20 ); } @Bean(value = "customName") public Person person () { lisi(); return new Person ("wangwu" , 30 ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Test public void annotationConfigTest () { ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (BeanConfig.class); BeanConfig beanConfig = (BeanConfig) ac.getBean("beanConfig" ); Person lisi = beanConfig.lisi(); }
解析配置类 什么是配置类? 通常情况下,我们称被 Configuration 注解标注的类为配置类。事实上,配置类的范围比这个定义稍微广泛一些,可以划分为全配置类和精简配置类。在解析配置类时,我们再进一步说明。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (BeanConfig.class);public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (Class<?>... annotatedClasses) { this (); register(annotatedClasses); refresh(); }
本文不详细介绍配置类本身如何注册到 BeanFactory 中。当 BeanConfig 被传递给 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,自身会先被解析为 BeanDefinition 注册到 beanFactory 中。有两点需要注意:
annotatedClasses 可以传入多个,意味着一开始静态指定的配置类 可以有多个。annotatedClasses 除了在命名上提示用户应传入被注解的类外,register(annotatedClasses) 实际上只是将它们视作普通的 Bean 注册到 beanFactory 中。它们是从外界传入的首批 BeanDefinition 。
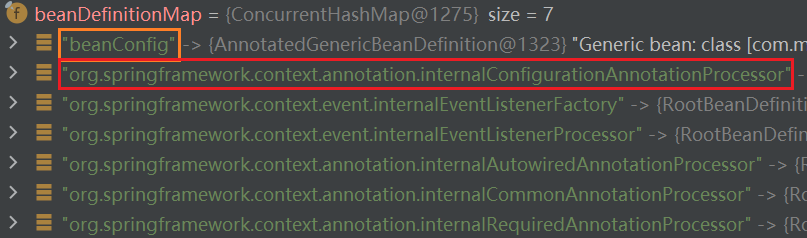
之后 Spring 进入 refresh 流程。使用 IDEA Debug 观察此时的 beanDefinitionMap,除了 beanConfig 外,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 在创建时,已经自动注册了 6 个 bean 定义,其中一个就是我们今天的主角 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor -> org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。显而易见,此时配置类还未被处理得到新的 bean 定义。
配置类后处理器 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 配置类后处理器 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 实现了接口 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,也因此同时实现了接口 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。在Spring 应用 context 刷新流程 中,我们介绍过这两个接口,它们作为工厂后处理器,被用于 refresh 过程的调用工厂后处理器阶段 (invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory))。工厂后处理器的作用,一言以蔽之,允许自定义修改应用上下文中的 bean 定义。
配置类后处理器 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的具体作用可以概括为两点:
解析配置类中配置的 Bean,将它们的 bean 定义注册到 BeanFactory 中。
(如有必要)增强配置类
处理配置类的核心方法 processConfigBeanDefinitions 根据之前的介绍,进入 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory),ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 会先作为 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 被调用。
个人的理解是,先将 BeanFactory 视作 BeanDefinitionRegistry 注册好 BeanDefinition,再视作 BeanFactory 进行处理,有点预备好原材料再统一处理的意思。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry (BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry); }
核心方法 processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry) 冗长,个人建议无需过度关注细节(但同时个人感受是反复阅读和 Debug 确实有益于加深理解,看个人时间和精力)。
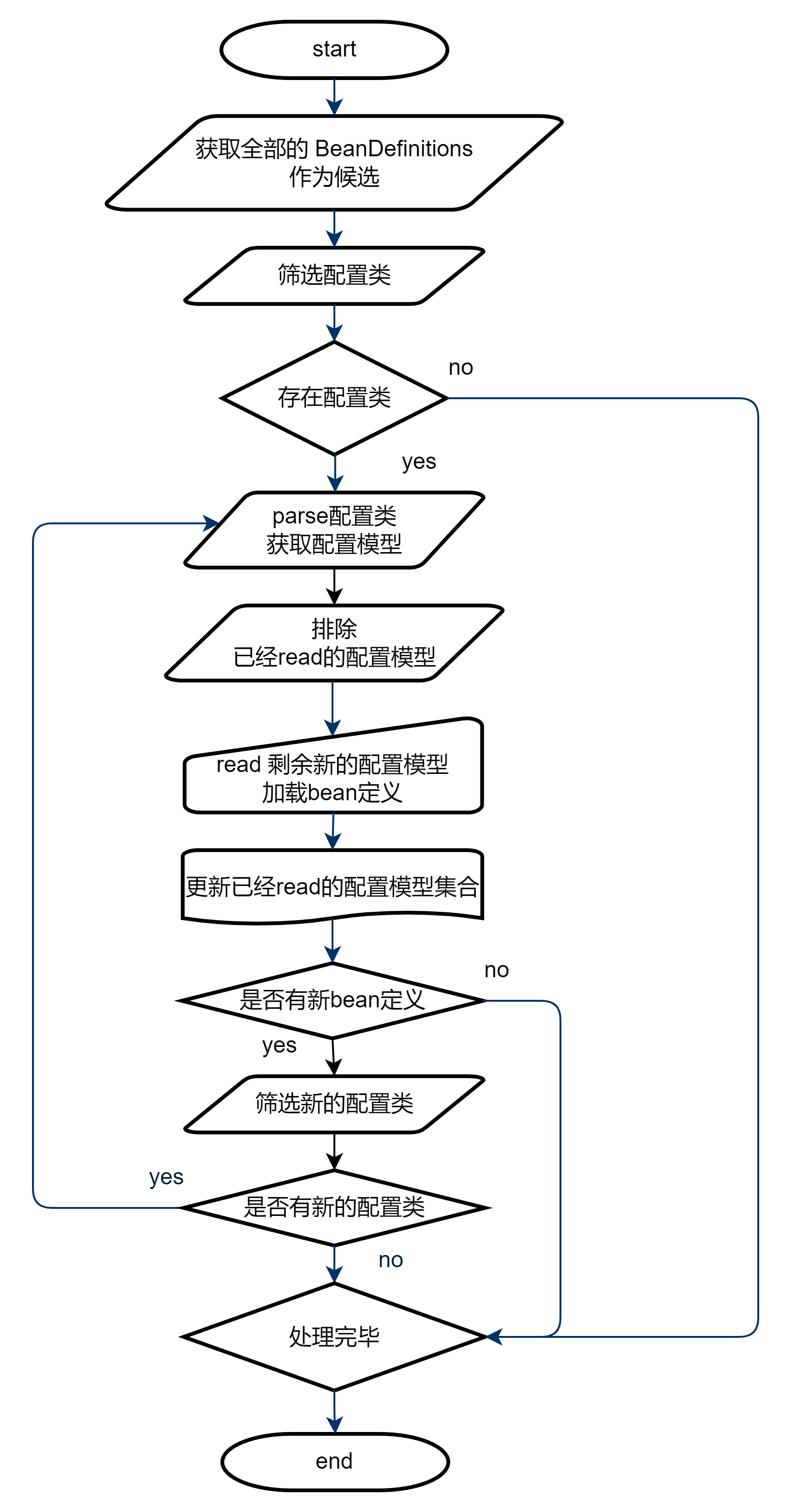
基于配置类的 BeanDefinition Registry(也就是 BeanFactory),获取配置类,构建和校验配置模型:
从 BeanDefinition Registry(即 BeanFactory)中查找配置类。
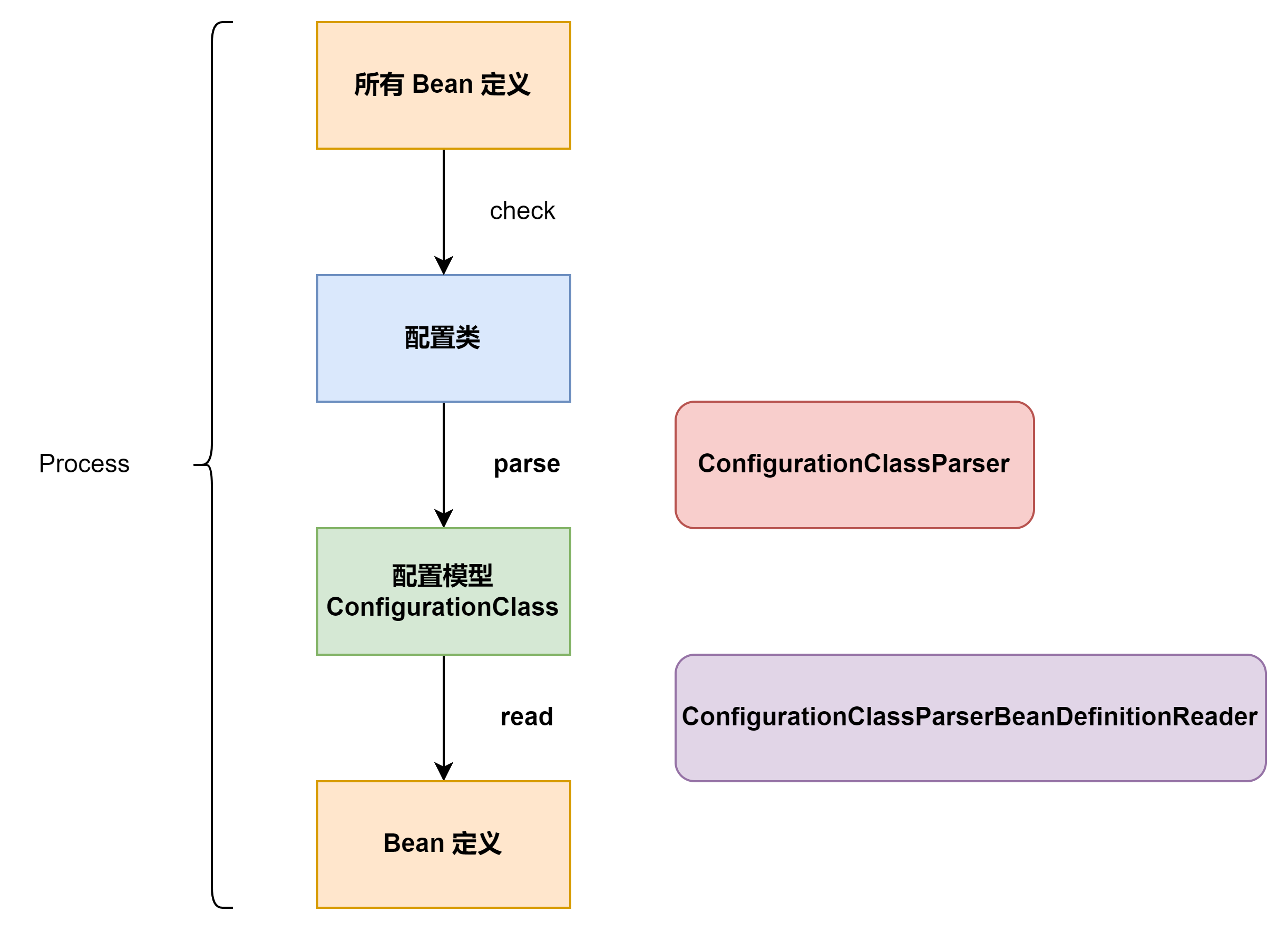
解析配置类得到配置模型 ,从模型中读取 BeanDefinitions 注册到 BeanDefinition Registry。
新的 BeanDefinitions 可能有新的配置类,回到 1 再来一遍。重复循环直到不再引入新的配置类。
以本文示例进行说明,静态添加的配置类只有 BeanConfig,假如 BeanConfig 不仅被 Configuration 注解标注,还被 ComponentScan 注解标注,并且刚好 Spring 通过扫描获得并添加了新的配置类,那么新的配置类就需要继续被解析。
应正视配置模型 这个概念,它可以理解为配置类到 BeanDefinitions 的中间产物。最初我先入为主,带着解析得到 BeanDefinitions 这样“一阶段”完成的观念,非常不理解 processConfigBeanDefinitions 方法上 Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of Configuration classes 这句注释。先行强调注意,处理配置类得到 bean 定义分为“两阶段”,解析配置类得到配置模型,从配置模型中读取 bean 定义 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 public void processConfigBeanDefinitions (BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList <BeanDefinitionHolder>(); String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String beanName : candidateNames) { BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef); } } else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this .metadataReaderFactory)) { configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder (beanDef, beanName)); } } if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) { return ; } Collections.sort(configCandidates, new Comparator <BeanDefinitionHolder>() { @Override public int compare (BeanDefinitionHolder bd1, BeanDefinitionHolder bd2) { int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition()); int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition()); return (i1 < i2) ? -1 : (i1 > i2) ? 1 : 0 ; } }); SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null ; if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) { sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry; if (!this .localBeanNameGeneratorSet && sbr.containsSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR)) { BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR); this .componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator; this .importBeanNameGenerator = generator; } } ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser ( this .metadataReaderFactory, this .problemReporter, this .environment, this .resourceLoader, this .componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet <BeanDefinitionHolder>(configCandidates); Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet <ConfigurationClass>(configCandidates.size()); do { parser.parse(candidates); parser.validate(); Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet <ConfigurationClass>(parser.getConfigurationClasses()); configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed); if (this .reader == null ) { this .reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader ( registry, this .sourceExtractor, this .resourceLoader, this .environment, this .importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry()); } this .reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses); alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses); candidates.clear(); if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) { String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet <String>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames)); Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet <String>(); for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) { alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); } for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) { if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) { BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this .metadataReaderFactory) && !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) { candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder (bd, candidateName)); } } } candidateNames = newCandidateNames; } } while (!candidates.isEmpty()); if (sbr != null ) { if (!sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) { sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry()); } } if (this .metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) { ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this .metadataReaderFactory).clearCache(); } }
判断是否是配置类 checkConfigurationClassCandidate 方法:
不能 className 为 null 或 Bean 定义拥有工厂方法
被 Configuration 注解标注(全配置类)
被 Component、ComponentScan、Import、ImportResource 注解标注或者拥有被 Bean 注解标注的方法
设置 order 用于排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate (BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) { String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName(); if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null ) { return false ; } AnnotationMetadata metadata; if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition && className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) { metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata(); } else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) { Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass(); metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata (beanClass, true ); } else { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className); metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); } catch (IOException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " + className, ex); } return false ; } } if (isFullConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL); } else if (isLiteConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE); } else { return false ; } Map<String, Object> orderAttributes = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(Order.class.getName()); if (orderAttributes != null ) { beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, orderAttributes.get(AnnotationUtils.VALUE)); } return true ; }
判断是否属于 Full 配置类
被 Configuration 注解标注
1 2 3 public static boolean isFullConfigurationCandidate (AnnotationMetadata metadata) { return metadata.isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName()); }
判断是否属于 Lite 配置类
被 Component、ComponentScan、Import、ImportResource 注解标注
拥有被 Bean 注解标注的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public static boolean isLiteConfigurationCandidate (AnnotationMetadata metadata) { if (metadata.isInterface()) { return false ; } for (String indicator : candidateIndicators) { if (metadata.isAnnotated(indicator)) { return true ; } } try { return metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName()); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to introspect @Bean methods on class [" + metadata.getClassName() + "]: " + ex); } return false ; } }
循环处理直至没有新增配置类 循环处理部分的代码有点难阅读。
首先是因为命名比较相似,需要理清各个变量的含义和作用
candidateNames 就是普普通通的纯候选者(全部 BeanDefinitions),每次循环在解析完,加载 BeanDefinitions 后可能会新增configCandidates(candidates) 就是符合配置类条件的配置类。虽然命名带 Candidates,其实已经是正牌,并非候选。感觉 configClass 更容易理解,但该变量名另作他用。有新增就要继续循环configClass(ConfigurationClass 类) 是经过解析的配置模型,不要和配置类搞混了。后面出现过 ConfigurationModel,感觉该命名更加准确
其次是因为对黑盒 parser 的作用不了解,个人经验如果完全将 parser 当作黑盒对待,不了解解析过程、解析的返回结果以及如何处理返回结果,理解循环解析的过程时会有点困难
parser.parse(candidates) 解析配置类构建得到配置模型(ConfigurationClass)。以副作用的形式进行处理,传入 ConfigurationClass,返回 ConfigurationClassthis.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses) 从配置模型(ConfigurationClass)中加载 BeanDefinitions
再次提示:正视配置模型的概念,ConfigurationClassParser 使用配置类构建配置模型并校验;ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader 从配置模型中读取 bean 定义。
解析配置类构建配置模型 parser.parse(candidates) 正式进入解析过程,ConfigurationClassParser 负责将配置类转换为配置模型(ConfigurationClass)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public void parse (Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) { this .deferredImportSelectors = new LinkedList <DeferredImportSelectorHolder>(); for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) { BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition(); try { if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName()); } else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) { parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName()); } else { parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException ( "Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]" , ex); } } processDeferredImportSelectors(); }
每次都创建一个新的配置模型 ConfigurationClass,最终处理结果以副作用的形式直接表现在配置模型上。
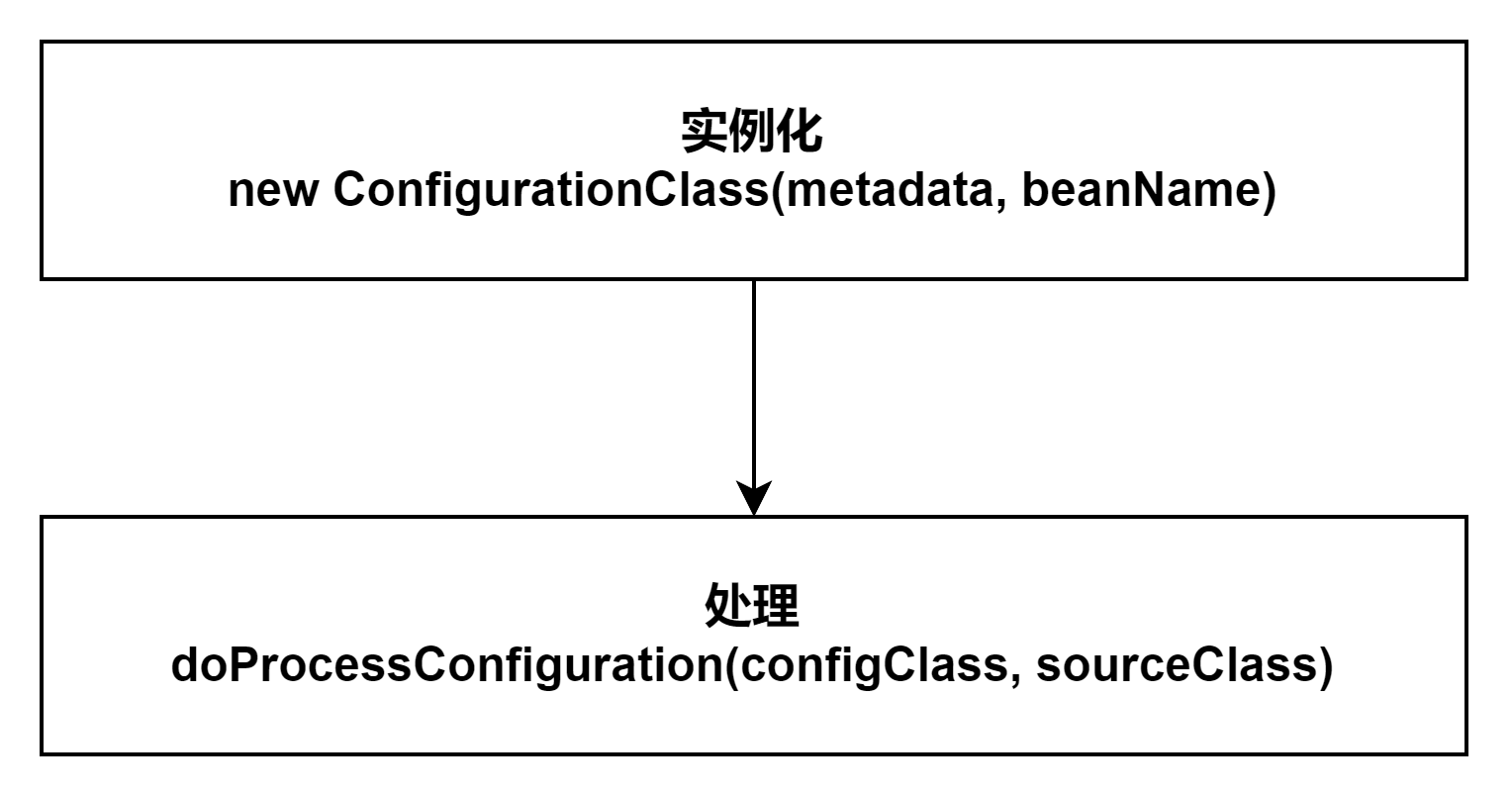
1 2 3 4 protected final void parse (AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException { processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass (metadata, beanName)); }
处理配置模型的方法 processConfigurationClass。
检查配置模型是否曾经处理过
处理配置模型(递归处理配置类和它的父类)
SourceClass 是一个简单的包装器,无论带注解的源类是如何被加载的,允许以统一的方式处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 protected void processConfigurationClass (ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException { if (this .conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) { return ; } ConfigurationClass existingClass = this .configurationClasses.get(configClass); if (existingClass != null ) { if (configClass.isImported()) { if (existingClass.isImported()) { existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass); } return ; } else { this .configurationClasses.remove(configClass); for (Iterator<ConfigurationClass> it = this .knownSuperclasses.values().iterator(); it.hasNext();) { if (configClass.equals(it.next())) { it.remove(); } } } } SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass); do { sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass); } while (sourceClass != null ); this .configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass); }
注意 ConfigurationClass 重写了 equals 和 hashCode 方法,metadata 的 className 相同代表配置模型也相同。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public boolean equals (Object other) { return (this == other || (other instanceof ConfigurationClass && getMetadata().getClassName().equals(((ConfigurationClass) other).getMetadata().getClassName()))); } public int hashCode () { return getMetadata().getClassName().hashCode(); }
真正处理配置模型的方法,根据注释很容易知道,如果配置类携带了 PropertySource、ComponentScan、Import、ImportResource、Bean 等注解,就是在这里被处理的。Bean 注解标注的方法,configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass)) 将它以 BeanMethod 的形式添加到配置模型中。
先递归的处理成员(嵌套)类
处理 @PropertySource
处理 @ComponentScan
处理 @Import
处理 @ImportResource
处理 @Bean,使用 ASM 代替 JVM 反射,以获得确定性的声明顺序
处理接口的默认方法
检查是否有父类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass (ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException { processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass); for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class, org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) { if (this .environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) { processPropertySource(propertySource); } else { logger.warn("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment" ); } } Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class); if (!componentScans.isEmpty() && !this .conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) { for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) { Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions = this .componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) { if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate( holder.getBeanDefinition(), this .metadataReaderFactory)) { parse(holder.getBeanDefinition().getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } } } processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true ); if (sourceClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(ImportResource.class.getName())) { AnnotationAttributes importResource = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class); String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations" ); Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader > readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader" ); for (String resource : resources) { String resolvedResource = this .environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource); configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass); } } Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass); for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) { configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod (methodMetadata, configClass)); } processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass); if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) { String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName(); if (!superclass.startsWith("java" ) && !this .knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) { this .knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass); return sourceClass.getSuperClass(); } } return null ; }
读取配置模型,加载 Bean 定义 this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses) 读取配置模型的内容,注册 BeanDefinitions 到 BeanDefinition Registry(也就是 BeanFactory)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void loadBeanDefinitions (Set<ConfigurationClass> configurationModel) { TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator = new TrackedConditionEvaluator (); for (ConfigurationClass configClass : configurationModel) { loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(configClass, trackedConditionEvaluator); } }
处理单独的一个配置模型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass (ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) { if (trackedConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass)) { String beanName = configClass.getBeanName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this .registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { this .registry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName); } this .importRegistry.removeImportingClass(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); return ; } if (configClass.isImported()) { registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass); } for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) { loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod); } loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources()); loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars()); }
增强配置类 我们在介绍 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 时提过,它既实现了接口 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,也因此同时实现了接口 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。在 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory) 阶段,调用 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法,成功注册配置类引入的 Bean 后,紧接着会调用 postProcessBeanFactory 方法,增强配置类本身。
ConfigurationClasses 在之前还是指配置模型,这里就又指配置类了。。。真让人头秃。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public void postProcessBeanFactory (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor (beanFactory)); }
增强所有 Full 类型配置类
查找所有 Full 类型的配置类
依次使用 ConfigurationClassEnhancer 增强目标类,成功则替换 BeanClass(不成功的情况是已经增强过)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public void enhanceConfigurationClasses (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap <String, AbstractBeanDefinition>(); for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException ("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass" ); } else if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) { logger.warn("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " + "is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " + "return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'." ); } configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef); } } if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty()) { return ; } ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer (); for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) { AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue(); beanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE); try { Class<?> configClass = beanDef.resolveBeanClass(this .beanClassLoader); Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this .beanClassLoader); if (configClass != enhancedClass) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(String.format("Replacing bean definition '%s' existing class '%s' with " + "enhanced class '%s'" , entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName())); } beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass); } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Cannot load configuration class: " + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex); } } }
如果增强过则不再处理。这往往代表容器中存在多个 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,虽然无害,但是建议调整配置
如果未曾增强过,则创建增强类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public Class<?> enhance(Class<?> configClass, ClassLoader classLoader) { if (EnhancedConfiguration.class.isAssignableFrom(configClass)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(String.format("Ignoring request to enhance %s as it has " + "already been enhanced. This usually indicates that more than one " + "ConfigurationClassPostProcessor has been registered (e.g. via " + "<context:annotation-config>). This is harmless, but you may " + "want check your configuration and remove one CCPP if possible" , configClass.getName())); } return configClass; } Class<?> enhancedClass = createClass(newEnhancer(configClass, classLoader)); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(String.format("Successfully enhanced %s; enhanced class name is: %s" , configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName())); } return enhancedClass; }
创建 CGLib 子类
如果完全不熟悉 CGLib,可以单独查阅一下相关资料,稍作了解。
创建 Enhancer,并设置属性。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private Enhancer newEnhancer (Class<?> superclass, ClassLoader classLoader) { Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer (); enhancer.setSuperclass(superclass); enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class <?>[] {EnhancedConfiguration.class}); enhancer.setUseFactory(false ); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); enhancer.setStrategy(new BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy (classLoader)); enhancer.setCallbackFilter(CALLBACK_FILTER); enhancer.setCallbackTypes(CALLBACK_FILTER.getCallbackTypes()); return enhancer; }
所有因为 Configuration 注解而被增强的配置类,它的 CGLib 子类都实现了这个标记接口,用于检查候选类是否已经增强过,避免重复增强。
该接口继承了 BeanFactoryAware。创建得到的 CGLib 子类必须能够访问 BeanFactory ,用以在工厂方法交叉调用时获取已经创建的 Bean 而非真正执行。
1 2 public interface EnhancedConfiguration extends BeanFactoryAware {}
创建子类,并注册静态回调。
1 2 3 4 5 6 private Class<?> createClass(Enhancer enhancer) { Class<?> subclass = enhancer.createClass(); Enhancer.registerStaticCallbacks(subclass, CALLBACKS); return subclass; }
CALLBACKS、CALLBACK_FILTER 和 $$beanFactory 属性名都是 ConfigurationClassEnhancer 的静态属性。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class ConfigurationClassEnhancer { private static final Callback[] CALLBACKS = new Callback [] { new BeanMethodInterceptor (), new BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor (), NoOp.INSTANCE }; private static final ConditionalCallbackFilter CALLBACK_FILTER = new ConditionalCallbackFilter (CALLBACKS); private static final String BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD = "$$beanFactory" ; }
匹配回调 ConditionalCallbackFilter ConditionalCallbackFilter 实现了 CGLib 的 CallbackFilter 接口,accept 方法返回准备使用的 Callback 的索引。匹配规则如下:
遍历 callbacks,依次判断
如果 this.callbacks[i] 不是 ConditionalCallback 类型,直接返回。根据 CALLBACKS 的值,这意味着没有匹配到合适的 MethodInterceptor,选择 NoOp.INSTANCE。
如果 this.callbacks[i] 是 ConditionalCallback 类型,使用 isMatch 方法判断是否匹配,匹配成功返回对应索引
Callback 中除了 NoOp.INSTANCE,还有 BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor 用于拦截 setBeanFactory 方法,以及 BeanMethodInterceptor 拦截 @Bean 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private static class ConditionalCallbackFilter implements CallbackFilter { private final Callback[] callbacks; private final Class<?>[] callbackTypes; public ConditionalCallbackFilter (Callback[] callbacks) { this .callbacks = callbacks; this .callbackTypes = new Class <?>[callbacks.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < callbacks.length; i++) { this .callbackTypes[i] = callbacks[i].getClass(); } } @Override public int accept (Method method) { for (int i = 0 ; i < this .callbacks.length; i++) { if (!(this .callbacks[i] instanceof ConditionalCallback) || ((ConditionalCallback) this .callbacks[i]).isMatch(method)) { return i; } } throw new IllegalStateException ("No callback available for method " + method.getName()); } public Class<?>[] getCallbackTypes() { return this .callbackTypes; } }
拦截 setBeanFactory 方法 BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor 实现了 MethodInterceptor 和 ConditionalCallback 接口。isMatch 匹配到 BeanFactoryAware 接口的 setBeanFactory 方法,则调用 intercept 方法,为 $$beanFactory 属性赋值。$$beanFactory 是 CGLib 生成的 BeanFactory 类型的属性。这个属性是通过设置 enhancer.setStrategy(new BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader)) 生成的。
这样,当配置类 Bean 被创建时,会因为实现了 BeanFactoryAware,在初始化阶段被调用 setBeanFactory 方法而被拦截。拦截后将获得的 beanFactory 实例保存在 CGlib 生成的属性 $$beanFactory 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private static class BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor , ConditionalCallback { @Override public Object intercept (Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable { Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(obj.getClass(), BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD); Assert.state(field != null , "Unable to find generated BeanFactory field" ); field.set(obj, args[0 ]); if (BeanFactoryAware.class.isAssignableFrom(ClassUtils.getUserClass(obj.getClass().getSuperclass()))) { return proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args); } return null ; } @Override public boolean isMatch (Method candidateMethod) { return (candidateMethod.getName().equals("setBeanFactory" ) && candidateMethod.getParameterTypes().length == 1 && BeanFactory.class == candidateMethod.getParameterTypes()[0 ] && BeanFactoryAware.class.isAssignableFrom(candidateMethod.getDeclaringClass())); } }
生成 $$beanFactory 属性 BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy 为配置的 CGLib 子类生成一个访问控制符为 public、类型为 BeanFactory、名称为 $$beanFactory 的属性。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 private static class BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy extends DefaultGeneratorStrategy { private final ClassLoader classLoader; public BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy (ClassLoader classLoader) { this .classLoader = classLoader; } @Override protected ClassGenerator transform (ClassGenerator cg) throws Exception { ClassEmitterTransformer transformer = new ClassEmitterTransformer () { @Override public void end_class () { declare_field(Constants.ACC_PUBLIC, BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD, Type.getType(BeanFactory.class), null ); super .end_class(); } }; return new TransformingClassGenerator (cg, transformer); } @Override public byte [] generate(ClassGenerator cg) throws Exception { if (this .classLoader == null ) { return super .generate(cg); } Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread(); ClassLoader threadContextClassLoader; try { threadContextClassLoader = currentThread.getContextClassLoader(); } catch (Throwable ex) { return super .generate(cg); } boolean overrideClassLoader = !this .classLoader.equals(threadContextClassLoader); if (overrideClassLoader) { currentThread.setContextClassLoader(this .classLoader); } try { return super .generate(cg); } finally { if (overrideClassLoader) { currentThread.setContextClassLoader(threadContextClassLoader); } } } }
核心:拦截 @Bean 方法 BeanMethodInterceptor 实现了 MethodInterceptor 和 ConditionalCallback 接口。isMatch 匹配到被 Bean 注解标注的方法,则调用 intercept 方法。被 Configuration 注解标注的配置类,它定义的被 Bean 注解标注的方法,只会在第一次被调用时真正地执行并创建实例,后续不会再执行的“魔法”就在这里。即使你手动地调用配置类的方法,或是被 Bean 注解标注的方法间互相调用,都是如此。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public Object intercept (Object enhancedConfigInstance, Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs, MethodProxy cglibMethodProxy) throws Throwable { ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(enhancedConfigInstance); String beanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(beanMethod); Scope scope = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(beanMethod, Scope.class); if (scope != null && scope.proxyMode() != ScopedProxyMode.NO) { String scopedBeanName = ScopedProxyCreator.getTargetBeanName(beanName); if (beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(scopedBeanName)) { beanName = scopedBeanName; } } if (factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName) && factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, beanName)) { Object factoryBean = beanFactory.getBean(BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); if (factoryBean instanceof ScopedProxyFactoryBean) { } else { return enhanceFactoryBean(factoryBean, beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanFactory, beanName); } } if (isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod)) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())) { logger.warn(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s is non-static and returns an object " + "assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will " + "result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, " + "@Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring " + "@Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid " + "these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details." , beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName())); } return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs); } return obtainBeanInstanceFromFactory(beanMethod, beanMethodArgs, beanFactory, beanName); }
isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod) 检查 beanMethod 是不是当前正在被调用的 FactoryMethod如果是,则调用实际的父类方法,创建 Bean 实例
如果不是,则从 BeanFactory 中获取
以本文示例进行说明。
调用 lisi() 前,设置当前正在调用的 FactoryMethod 为 lisi()
lisi() 调用被拦截后,查询获知当前正在调用的 FactoryMethod 确实是 lisi(),调用父类方法创建
调用 person() 前,设置当前正在调用的 FactoryMethod 为 person()
person() 调用被拦截后,查询获知当前正在调用的 FactoryMethod 确实是 person(),调用父类方法创建父类方法内调用了 lisi()
lisi() 调用被拦截后,查询获知当前正在调用的 FactoryMethod 是 person(),从 BeanFactory 中获取从 BeanFactory 中获取得到已经创建的 lisi
继续创建并返回
以上处理的过程是比较清晰简单的,但是当前正在被调用的 FactoryMethod 是什么时候保存的,怎么处理的,还未明朗。
isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod 判断是否是当前正在被调用的 FactoryMethod。
1 2 3 4 5 private boolean isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod (Method method) { Method currentlyInvoked = SimpleInstantiationStrategy.getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(); return (currentlyInvoked != null && method.getName().equals(currentlyInvoked.getName()) && Arrays.equals(method.getParameterTypes(), currentlyInvoked.getParameterTypes())); }
原理是通过 ThreadLocal 记录正在调用的 FactoryMethod。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class SimpleInstantiationStrategy implements InstantiationStrategy { private static final ThreadLocal<Method> currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod = new ThreadLocal <Method>(); public static Method getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod () { return currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.get(); } }
这里只是通过 get 获取 currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod 的值,我们还不知道它是在哪更新的。
currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod 的“来龙去脉” 当 BeanFactory 创建 Bean 实例时,被 Bean 注解标注的方法注册的 Bean 在实例化时是使用工厂方法而不是构造器方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance (String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) { if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null ) { return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args); } } protected BeanWrapper instantiateUsingFactoryMethod ( String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] explicitArgs) { return new ConstructorResolver (this ).instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, explicitArgs); }
BeanFactory 委托给 ConstructorResolver。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public BeanWrapper instantiateUsingFactoryMethod ( final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] explicitArgs) { beanInstance = this .beanFactory.getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate( mbd, beanName, this .beanFactory, factoryBean, factoryMethodToUse, argsToUse); }
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的 instantiationStrategy 类型是 CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy,继承自 SimpleInstantiationStrategy。
1 private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy ();
SimpleInstantiationStrategy 的 instantiate 方法在通过反射调用 factoryBean 对应的 method 前后,会处理 currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod 的值。
被 Bean 注解标注的方法,对应的 Bean 就是一个 FactoryBean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public class SimpleInstantiationStrategy implements InstantiationStrategy { @Override public Object instantiate (RootBeanDefinition bd, String beanName, BeanFactory owner, Object factoryBean, final Method factoryMethod, Object... args) { try { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null ) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction <Object>() { @Override public Object run () { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(factoryMethod); return null ; } }); } else { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(factoryMethod); } Method priorInvokedFactoryMethod = currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.get(); try { currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.set(factoryMethod); return factoryMethod.invoke(factoryBean, args); } finally { if (priorInvokedFactoryMethod != null ) { currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.set(priorInvokedFactoryMethod); } else { currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.remove(); } } } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException (factoryMethod, "Illegal arguments to factory method '" + factoryMethod.getName() + "'; " + "args: " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(args), ex); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException (factoryMethod, "Cannot access factory method '" + factoryMethod.getName() + "'; is it public?" , ex); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { String msg = "Factory method '" + factoryMethod.getName() + "' threw exception" ; if (bd.getFactoryBeanName() != null && owner instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory && ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) owner).isCurrentlyInCreation(bd.getFactoryBeanName())) { msg = "Circular reference involving containing bean '" + bd.getFactoryBeanName() + "' - consider " + "declaring the factory method as static for independence from its containing instance. " + msg; } throw new BeanInstantiationException (factoryMethod, msg, ex.getTargetException()); } } }
从 BeanFactory 获取 Bean 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 private Object obtainBeanInstanceFromFactory (Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs, ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String beanName) { boolean alreadyInCreation = beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(beanName); try { if (alreadyInCreation) { beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, false ); } boolean useArgs = !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(beanMethodArgs); if (useArgs && beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) { for (Object arg : beanMethodArgs) { if (arg == null ) { useArgs = false ; break ; } } } Object beanInstance = (useArgs ? beanFactory.getBean(beanName, beanMethodArgs) : beanFactory.getBean(beanName)); if (beanInstance != null && !ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanInstance)) { String msg = String.format("@Bean method %s.%s called as a bean reference " + "for type [%s] but overridden by non-compatible bean instance of type [%s]." , beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName(), beanMethod.getReturnType().getName(), beanInstance.getClass().getName()); try { BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName); msg += " Overriding bean of same name declared in: " + beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { } throw new IllegalStateException (msg); } Method currentlyInvoked = SimpleInstantiationStrategy.getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(); if (currentlyInvoked != null ) { String outerBeanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(currentlyInvoked); beanFactory.registerDependentBean(beanName, outerBeanName); } return beanInstance; } finally { if (alreadyInCreation) { beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, true ); } } }
延续自本文的文章: