演示字节码指令的执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class ByteCodeTest_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = Short.MAX_VALUE + 1;
int c = a + b;
System.out.println(c);
}
}
|
操作数栈和本地变量表的大小
在编译期间就可计算得到操作数栈和本地变量表的大小。
1
| stack=2, locals=4, args_size=1
|
本地变量表
Slot,即槽位,可理解为索引。
1
2
3
4
5
| Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 18 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
3 15 1 a I
6 12 2 b I
10 8 3 c I
|
运行时常量池
1
2
3
| #3 = Integer 32768
#4 = Fieldref
#5 = Methodref
|
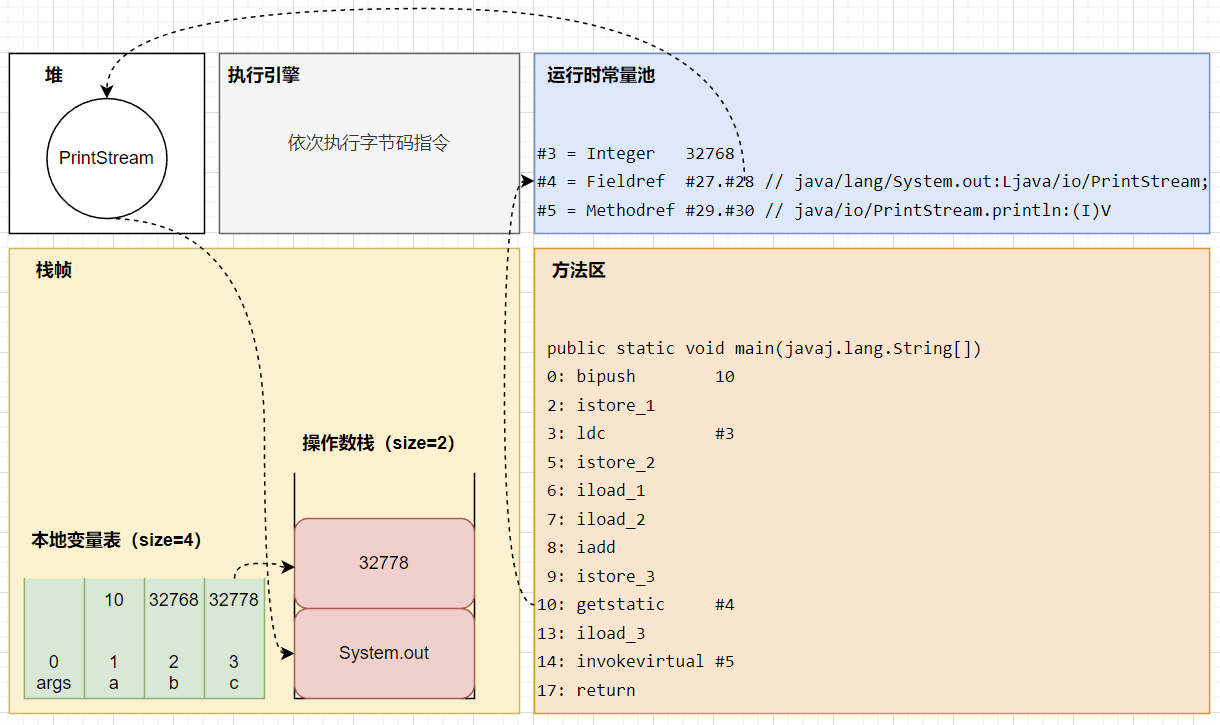
字节码指令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| 0: bipush 10
2: istore_1
3: ldc #3 // int 32768
5: istore_2
6: iload_1
7: iload_2
8: iadd
9: istore_3
10: getstatic #4 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
13: iload_3
14: invokevirtual #5 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(I)V
17: return
|
- bipush,将一个 byte,推入操作数栈。
- short 范围内的数是和字节码指令一起存储的,范围外的数是存储在运行时常量池中的。
- 操作数栈的宽度是 4 个字节,short 范围内的数在推入操作数栈前会经过符号扩展成为 int。
- istore_1,将栈顶的 int,存入局部变量表,槽位 1。
- ldc,从运行时常量池中将指定常量推入操作数栈。
- istore_2,将栈顶的 int,存入局部变量表,槽位 2。
- iload_1 iload_2,依次从局部变量表将两个 int 推入操作数栈,槽位分别是 1 和 2。
- iadd,将栈顶的两个 int 弹出并相加,将结果推入操作数栈。
- istore_3,将栈顶的 int,存入局部变量表,槽位 3。
- getstatic,获取类的静态属性,推入操作数栈。
- iload_3,从局部变量表将 int 推入操作数栈,槽位 3。
- invokevirtual,将栈顶的参数依次弹出,调用实例方法。
- return,返回 void
分析 a++ 和 ++a
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class ByteCodeTest_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = a++ + ++a + a--;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
|
字节码指令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 0: bipush 10
2: istore_1
3: iload_1
4: iinc 1, 1
7: iinc 1, 1
10: iload_1
11: iadd
12: iload_1
13: iinc 1, -1
16: iadd
17: istore_2
|
- a++ 和 ++a 的区别是先 load 还是先 iinc。
- iinc,将局部变量表指定槽位的数加上一个常数。
- 注意 a 只 load 到操作数栈并没有 store 回局部变量表。
- b = 10 + 12 + 12 = 34
- a = 10 + 1 + 1 - 1 = 11
分析判断条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class ByteCodeTest_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0;
if (a == 0) {
a = 10;
} else {
a = 20;
}
}
}
|
字节码指令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| 0: iconst_0
1: istore_1
2: iload_1
3: ifne 12
6: bipush 10
8: istore_1
9: goto 15
12: bipush 20
14: istore_1
15: return
|
- iconst,将一个 int 常量推入操作数栈。
- if
<cond>,一个 int 和 0 的比较成立时进入分支,跳转到指定行号。
- goto,总是进入的分支,跳转到指定行号。
涉及的字节码指令
- bipush,将一个 byte 符号扩展为一个 int,推入操作数栈。
- istore,将栈顶的 int,存入局部变量表的指定槽位。
- iload,将局部变量表指定槽位的 int,推入操作数栈。
- ldc,从运行时常量池将指定常量推入操作数栈。
- iadd,将栈顶的两个 int 弹出并相加,将结果推入操作数栈。
- getstatic,获取类的静态属性,推入操作数栈。
- invokevirtual,将栈顶的参数依次弹出,调用实例方法。
- return,返回 void。
- iinc,将局部变量表中指定槽位的数加一个常量。
- if
<cond>,一个 int 和 0 的比较成立时进入分支,跳转到指定行号。
- ifeq,equals
- ifne,not equals
- iflt,less than
- ifge,greater than or equals
- ifgt,great than
- ifle,less than or equals
- goto,总是进入的分支,跳转到指定行号。
