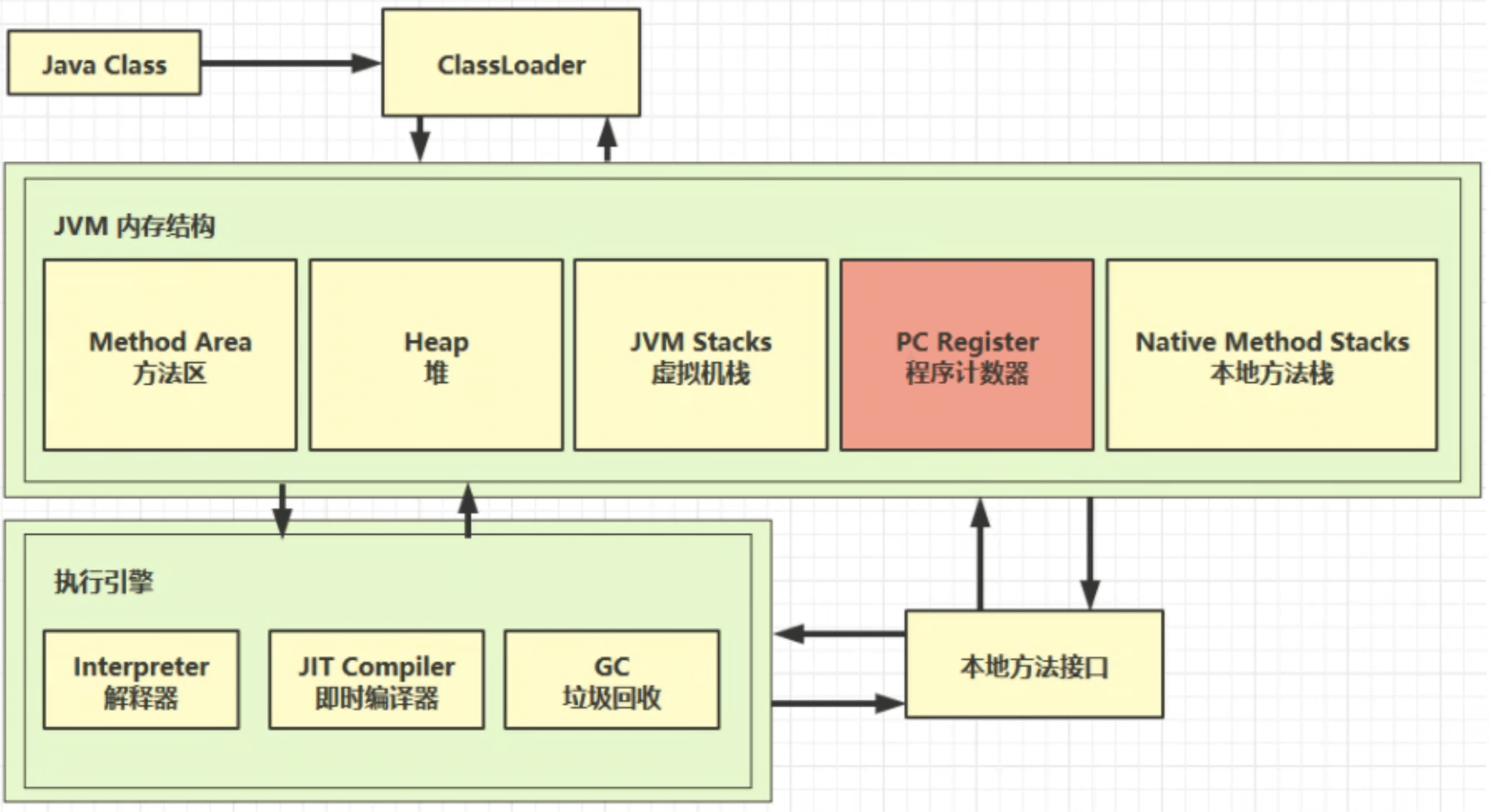
内存区域 JVM 内存区域划分为:
程序计数器 虚拟机栈 Java 虚拟机栈(Java Virtual Machine Stack),线程私有,生命周期与线程相同。虚拟机栈描述的是 Java 方法执行的线程内存模型。每个方法被执行的时候,Java虚拟机都会同步创建一个栈帧(Stack Frame)用于存储局部变量表、操作数栈、动态连接、方法出口等信息。
可以使用 -Xss1024k 设置虚拟机栈的大小。默认情况下都是 1024k,只有 Windows 中取决于虚拟内存。
栈内存溢出
栈帧过多导致栈内存溢出
栈帧过大导致栈内存溢出(难复现)
不正确的递归调用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class StackTest_4 { private static int count = 0 ; public static void main (String[] args) { try { method1(); } catch (Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println(count); } } private static void method1 () { count++; method1(); } }
循环引用导致 JSON 解析无限循环 并非只有自己写的递归方法可能引发栈内存溢出,有可能第三方库也会引发栈内存溢出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public class StackTest_5 { public static void main (String[] args) throws JsonProcessingException { Department department = new Department (); department.setName("Tech" ); Employee employee1 = new Employee (); employee1.setName("Tom" ); employee1.setDepartment(department); Employee employee2 = new Employee (); employee2.setName("Tim" ); employee2.setDepartment(department); department.setEmployees(Arrays.asList(employee1, employee2)); ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper (); System.out.println(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(department)); } static class Department { private String name; private List<Employee> employees; public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public List<Employee> getEmployees () { return employees; } public void setEmployees (List<Employee> employees) { this .employees = employees; } } static class Employee { private String name; private Department department; public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Department getDepartment () { return department; } public void setDepartment (Department department) { this .department = department; } } }
局部变量的线程安全问题
局部变量如果未逃离方法的作用范围,就是线程安全的。
局部变量如果是引用类型且逃离了方法的作用范围,就是线程不安全的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class StackTest_3 { public static void main (String[] args) { method1(); } private static void method1 () { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); sb.append(1 ); sb.append(2 ); sb.append(3 ); System.out.println(sb); } private static void method2 (StringBuilder sb) { sb.append(1 ); sb.append(2 ); sb.append(3 ); System.out.println(sb); } private static StringBuilder method3 () { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); sb.append(1 ); sb.append(2 ); sb.append(3 ); return sb; } }
线程问题排查 CPU 占用率居高不下 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class ThreadTest_1 { public static void main (String[] args) { new Thread (null , () -> { System.out.println("t1..." ); while (true ) { } }, "thread1" ).start(); new Thread (null , () -> { System.out.println("t2..." ); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "thread2" ).start(); new Thread (null , () -> { System.out.println("t3..." ); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "thread3" ).start(); } }
当发现 CPU 占用率居高不下时,可以尝试以下步骤:
top,定位 cpu 占用高的进程 id。ps H -eo pid,tid,%cpu | grep pid,进一步定位引起 cpu 占用高的线程 id。jstack pid,根据线程 id 换算成 16进制的 nid 找到对应线程,进一步定位到问题的源码行号。
1 2 3 4 5 "thread1" #8 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x00007f9bd0162800 nid=0x1061ad runnable [0x00007f9bd56eb000] java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE at com.moralok.jvm.thread.ThreadTest_1.lambda$main$0(ThreadTest_1.java:10) at com.moralok.jvm.thread.ThreadTest_1$$Lambda$1/250421012.run(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:750)
死锁,迟迟未返回结果 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class ThreadTest_2 { private static final Object A = new Object (); private static final Object B = new Object (); public static void main (String[] args) { new Thread (null , () -> { System.out.println("t1..." ); synchronized (A) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get A" ); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } synchronized (B) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get B" ); } } }, "thread1" ).start(); new Thread (null , () -> { System.out.println("t2..." ); synchronized (B) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get B" ); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } synchronized (A) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get A" ); } } }, "thread2" ).start(); } }
jstack pid,会显示找到死锁,以及死锁涉及的线程,,并各自持有的锁还有等待的锁。其他工具如 jconsole 也具有检测死锁的功能。
本地方法栈 堆 堆(Heap)的特点:
线程共享,需要考虑线程安全问题。
存在垃圾回收机制。
使用 -Xmx8m 设置大小。
堆内存溢出 既然堆有垃圾回收机制,为什么还会发生内存溢出呢?最开始的时候,我也有这样的困惑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class HeapTest_1 { public static void main (String[] args) { int i = 0 ; try { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); String s = "hello" ; while (true ) { list.add(s); s = s + s; i++; } } catch (Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("运行次数 " + i); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Arrays.java:3332) at java.lang.AbstractStringBuilder.ensureCapacityInternal(AbstractStringBuilder.java:124) at java.lang.AbstractStringBuilder.append(AbstractStringBuilder.java:448) at java.lang.StringBuilder.append(StringBuilder.java:141) at com.moralok.jvm.memory.heap.HeapTest_1.main(HeapTest_1.java:21) 运行次数 17
堆内存溢出的发生往往需要长时间的运行,因此在排查相关问题时,可以适当调小堆内存。
监测堆内存
使用 jps 查看 Java 进程列表
使用 jmap -heap pid 查看堆内存信息
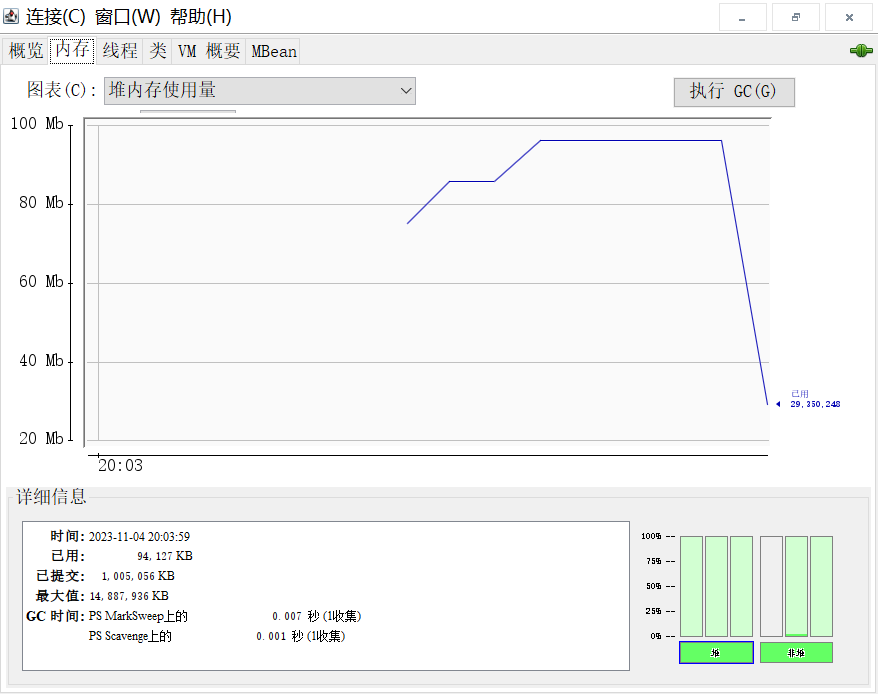
还可以使用 jconsole 观察堆内存变化曲线
还可以使用 VisualVM 查看堆信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class HeapTest_2 { public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("1..." ); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(30 ); byte [] bytes = new byte [1024 * 1024 * 10 ]; System.out.println("2..." ); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(30 ); bytes = null ; System.gc(); System.out.println("3..." ); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3000 ); } }
使用 jmap -heap pid 查看堆内存信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Eden Space: capacity = 268435456 (256.0MB) used = 32212360 (30.72010040283203MB) used = 42698136 (40.720115661621094MB) used = 5368728 (5.120018005371094MB)
使用 jconsole 查看堆内存信息:
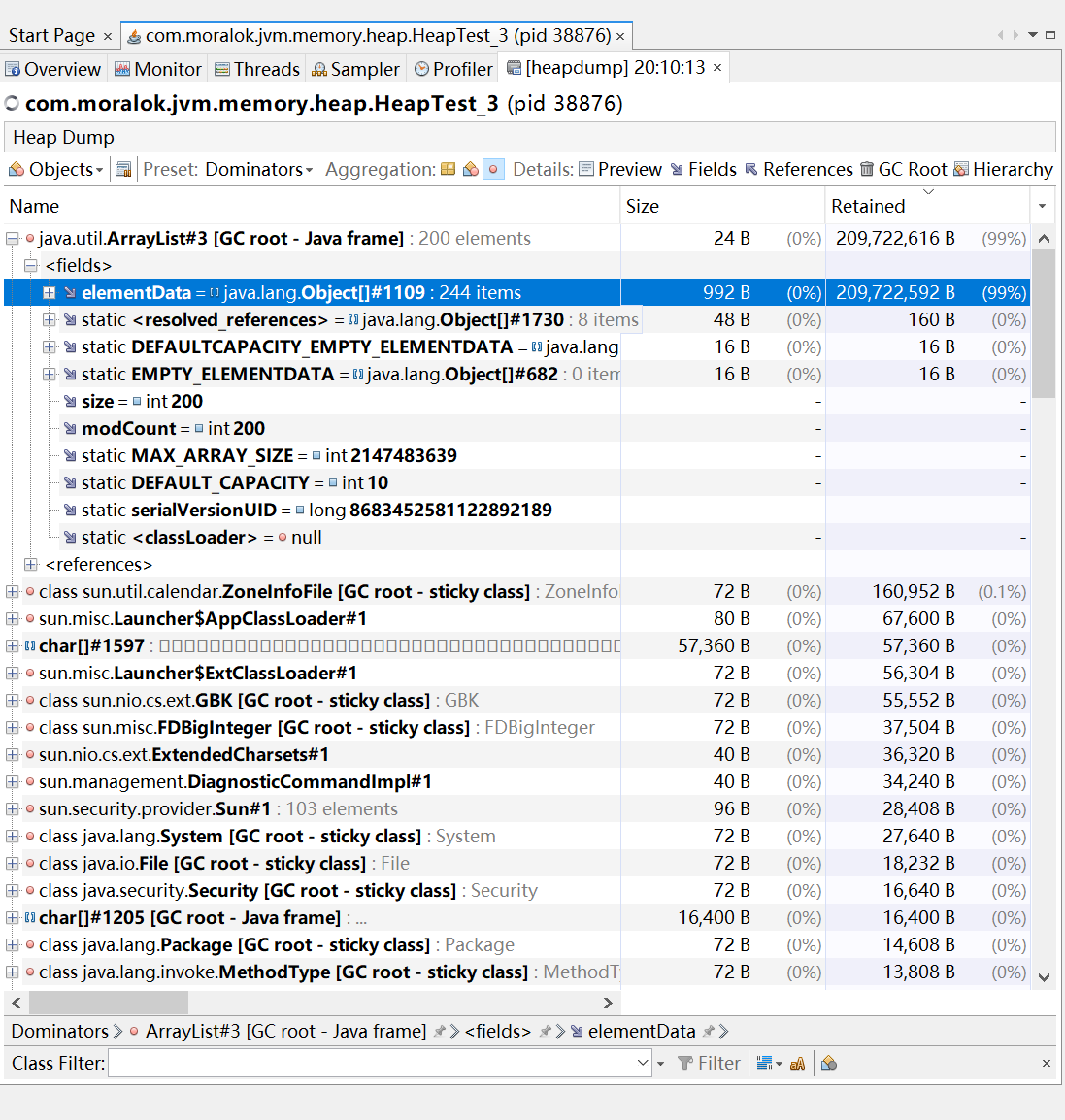
堆内存占用居高不下 当你发现堆内存占用居高不下,经过 GC,下降也不明显,如果你想查看一下堆内的具体情况,可以将其 dump 查看。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class HeapTest_3 { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { List<Student> students = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 200 ; i++) { students.add(new Student ()); } System.in.read(); } static class Student { private byte [] score = new byte [1024 * 1024 ]; } }
可使用 VisualVM 的 Heap Dump 功能:
也可使用 jmap -dump:format=b,file=filename.hprof pid,需要其他分析工具搭配。
方法区 根据《Java虚拟机规范》,方法区在逻辑上是堆的一部分,但是在具体实现上,各个虚拟机厂商并不相同。对于 Hotspot 而言:
JDK 8 之前,方法区的具体实现为永久代,使用堆内存,使用 -XX:MaxPermSize=10m 设置大小。
JDK 8 开始,方法区的具体实现为元空间,使用直接内存,使用 -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=10m 设置大小。
方法区溢出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class MethodAreaTest_1 extends ClassLoader { public static void main (String[] args) { int j = 0 ; try { MethodAreaTest_1 methodAreaTest1 = new MethodAreaTest_1 (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 20000 ; i++, j++) { ClassWriter classWriter = new ClassWriter (0 ); classWriter.visit(Opcodes.V1_8, Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, "Class" + i, null , "java/lang/Object" , null ); byte [] code = classWriter.toByteArray(); methodAreaTest1.defineClass("Class" + i, code, 0 , code.length); } } catch (ClassFormatError e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("次数 " + j); } } }
当设置的值太小时 -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=8m,提示 MaxMetaspaceSize is too small。
实验中抛出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Compressed class space。
添加参数 -XX:-UseCompressedClassPointers 后,抛出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace。
JDK 6 设置 -XX:MaxPermSize=8m,抛出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space。
不要认为自己不会写动态生成字节码相关的代码就忽略这方面的问题,如今很多框架使用字节码技术大量地动态生成类。
运行时常量池 二进制字节码文件主要包含三类信息:
类的基本信息
类的常量池(Constant Pool)
类的方法信息
使用 javap 反编译 1 2 3 4 5 6 public class MethodAreaTest_2 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("hello world" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 Classfile /C:/Users/username/Documents/github/jvm-study/target/classes/com/moralok/jvm/memory/methodarea/MethodAreaTest_2.class Last modified 2023-11-4; size 619 bytes MD5 checksum 0ed10a8f0a03be54fd4159958ee7446c Compiled from "MethodAreaTest_2.java" public class com.moralok.jvm.memory.methodarea.MethodAreaTest_2 minor version: 0 major version: 52 flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER Constant pool: # 1 = Methodref # 2 = Fieldref # 3 = String # 4 = Methodref # 5 = Class # 6 = Class # 7 = Utf8 <init> # 8 = Utf8 ()V # 9 = Utf8 Code # 10 = Utf8 LineNumberTable # 11 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable # 12 = Utf8 this # 13 = Utf8 Lcom/moralok/jvm/memory/methodarea/MethodAreaTest_2; # 14 = Utf8 main # 15 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V # 16 = Utf8 args # 17 = Utf8 [Ljava/lang/String; # 18 = Utf8 SourceFile # 19 = Utf8 MethodAreaTest_2.java # 20 = NameAndType # 21 = Class # 22 = NameAndType # 23 = Utf8 hello world # 24 = Class # 25 = NameAndType # 26 = Utf8 com/moralok/jvm/memory/methodarea/MethodAreaTest_2 # 27 = Utf8 java/lang/Object # 28 = Utf8 java/lang/System # 29 = Utf8 out # 30 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream; # 31 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream # 32 = Utf8 println # 33 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)V { public com.moralok.jvm.memory.methodarea.MethodAreaTest_2(); descriptor: ()V flags: ACC_PUBLIC Code: stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1 0: aload_0 1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V 4: return LineNumberTable: line 3: 0 LocalVariableTable: Start Length Slot Name Signature 0 5 0 this Lcom/moralok/jvm/memory/methodarea/MethodAreaTest_2; public static void main(java.lang.String[]); descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC Code: stack=2, locals=1, args_size=1 0: getstatic #2 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream; 3: ldc #3 // String hello world 5: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V 8: return LineNumberTable: line 6: 0 line 7: 8 LocalVariableTable: Start Length Slot Name Signature 0 9 0 args [Ljava/lang/String; } SourceFile: "MethodAreaTest_2.java"
Class 文件的常量池就是一张表,虚拟机根据索引去查找类名、字段名及其类型,方法名及其参数类型和字面量等。
当类被加载到虚拟机之后,Class 文件中的常量池中的信息就进入到了运行时常量池。
这个过程其实就是信息从文件进入了内存。
虚拟机解释器(interpreter)需要解释的字节码指令如下:
1 2 3 0: getstatic #2 3: ldc #3 5: invokevirtual #4
索引 #2 的意思就是去常量表里查找对应项代表的事物。
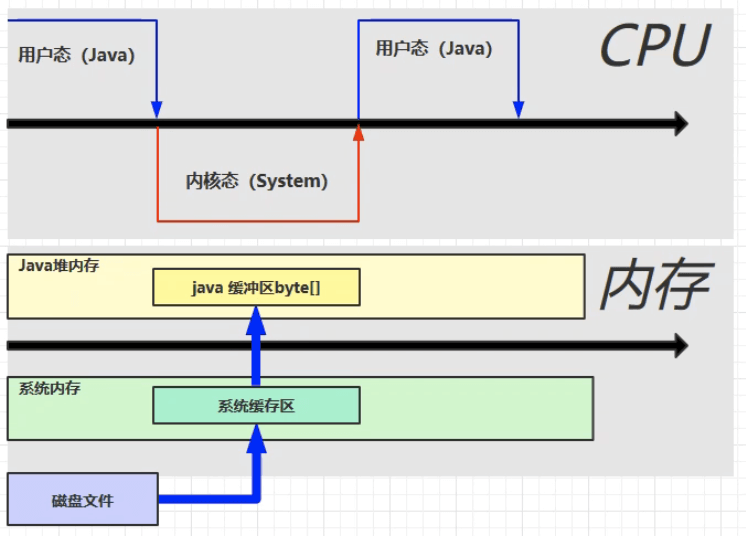
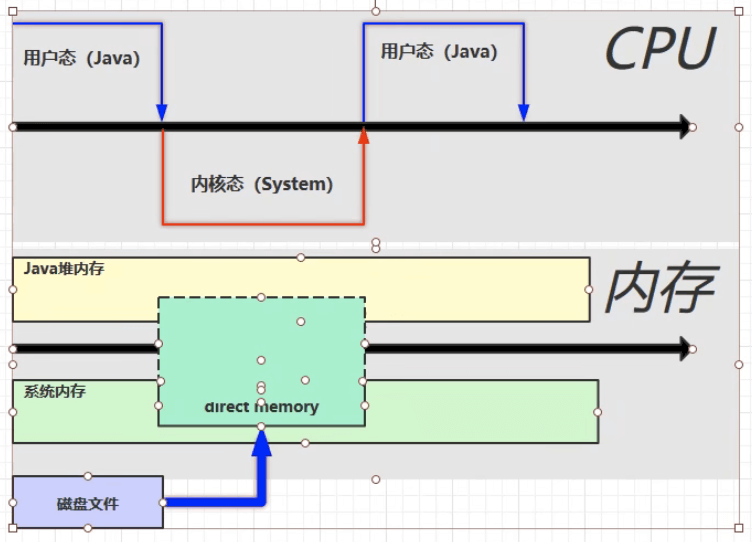
直接内存
常见于 NIO 操作中的数据缓冲区。
分配和回收的成本较高,但读写性能更高。
不由 JVM 进行内存释放
NIO 和 IO 的拷贝性能 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public class DirectMemoryTest_1 { private static final String FROM = "C:\\Users\\username\\Videos\\jellyfin\\media\\movies\\Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets (2002) [1080p]\\Harry.Potter.and.the.Chamber.of.Secrets.2002.1080p.BrRip.x264.YIFY.mp4" ; private static final String TO = "C:\\Users\\username\\Videos\\jellyfin\\media\\movies\\Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets (2002) [1080p]\\Harry.Potter.and.the.Chamber.of.Secrets.2002.1080p.BrRip.x264.YIFY-copy.mp4" ; private static final int _1Mb = 1024 * 1024 ; public static void main (String[] args) { io(); directBuffer(); } private static void directBuffer () { long start = System.nanoTime(); try (FileChannel from = new FileInputStream (FROM).getChannel(); FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream (TO).getChannel()) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Mb); while (true ) { int len = from.read(buffer); if (len == -1 ) { break ; } buffer.flip(); to.write(buffer); buffer.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } long end = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println("directBuffer 用时 " + (end - start) / 1000_000.0 ); } private static void io () { long start = System.nanoTime(); try (FileInputStream from = new FileInputStream (FROM); FileOutputStream to = new FileOutputStream (TO)) { byte [] buffer = new byte [_1Mb]; while (true ) { int len = from.read(buffer); if (len == -1 ) { break ; } to.write(buffer); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } long end = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println("io 用时 " + (end - start) / 1000_000.0 ); } }
1 2 io 用时 1676.9797 directBuffer 用时 836.4796
直接内存溢出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class DirectMemoryTest_2 { private static final int _100Mb = 1024 * 1024 * 100 ; public static void main (String[] args) { List<ByteBuffer> list = new ArrayList <>(); int i = 0 ; try { while (true ) { ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_100Mb); list.add(byteBuffer); i++; } } catch (Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(i); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Direct buffer memory at java.nio.Bits.reserveMemory(Bits.java:695) at java.nio.DirectByteBuffer.<init>(DirectByteBuffer.java:123) at java.nio.ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(ByteBuffer.java:311) at com.moralok.jvm.memory.direct.DirectMemoryTest_2.main(DirectMemoryTest_2.java:16) 145
这似乎是代码中抛出的异常,而不是真正的直接内存溢出?
直接内存释放的原理 演示直接内存的释放受 GC 影响 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class DirectMemoryTest_3 { private static final int _1GB = 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ; public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1GB); System.out.println("分配完毕" ); System.in.read(); System.out.println("开始释放" ); byteBuffer = null ; System.gc(); System.in.read(); } }
手动进行直接内存的分配和释放 在代码中实现手动进行直接内存的分配和释放。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class DirectMemoryTest_4 { private static final int _1GB = 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ; public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe(); long base = unsafe.allocateMemory(_1GB); unsafe.setMemory(base, _1GB, (byte ) 0 ); System.in.read(); unsafe.freeMemory(base); System.in.read(); } private static Unsafe getUnsafe () { try { Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe" ); f.setAccessible(true ); Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) f.get(null ); return unsafe; } catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } }
如何将 GC 和直接内存的分配和释放关联 本质上,直接内存的自动释放是利用了虚引用的机制,间接调用了 unsafe 的分配和释放直接内存的方法。
DirectByteBuffer 就是使用 unsafe.allocateMemory(size) 分配直接内存。DirectByteBuffer 对象以及一个 Deallocator 对象(Runnable 类型)一起用于创建了一个虚引用类型的 Cleaner 对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { try { base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size); } catch (OutOfMemoryError x) { Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap); throw x; } cleaner = Cleaner.create(this , new Deallocator (base, size, cap)); att = null ; }
根据虚引用的机制,如果 DirectByteBuffer 对象被回收,虚引用对象会被加入到 Cleanner 的引用队列,ReferenceHandler 线程会处理引用队列中的 Cleaner 对象,进而调用 Deallocator 对象的 run 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public void run () { if (address == 0 ) { return ; } unsafe.freeMemory(address); address = 0 ; Bits.unreserveMemory(size, capacity); }