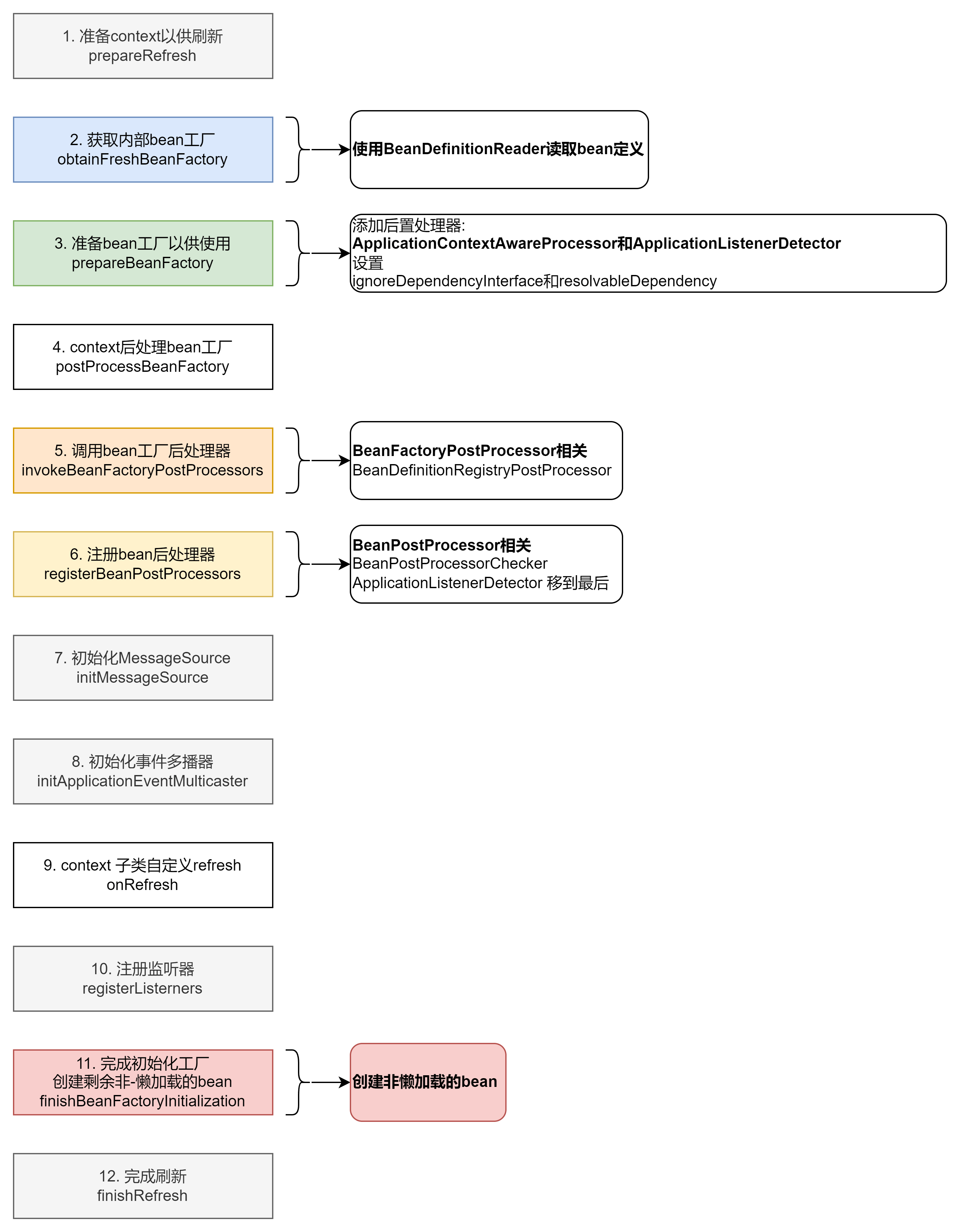
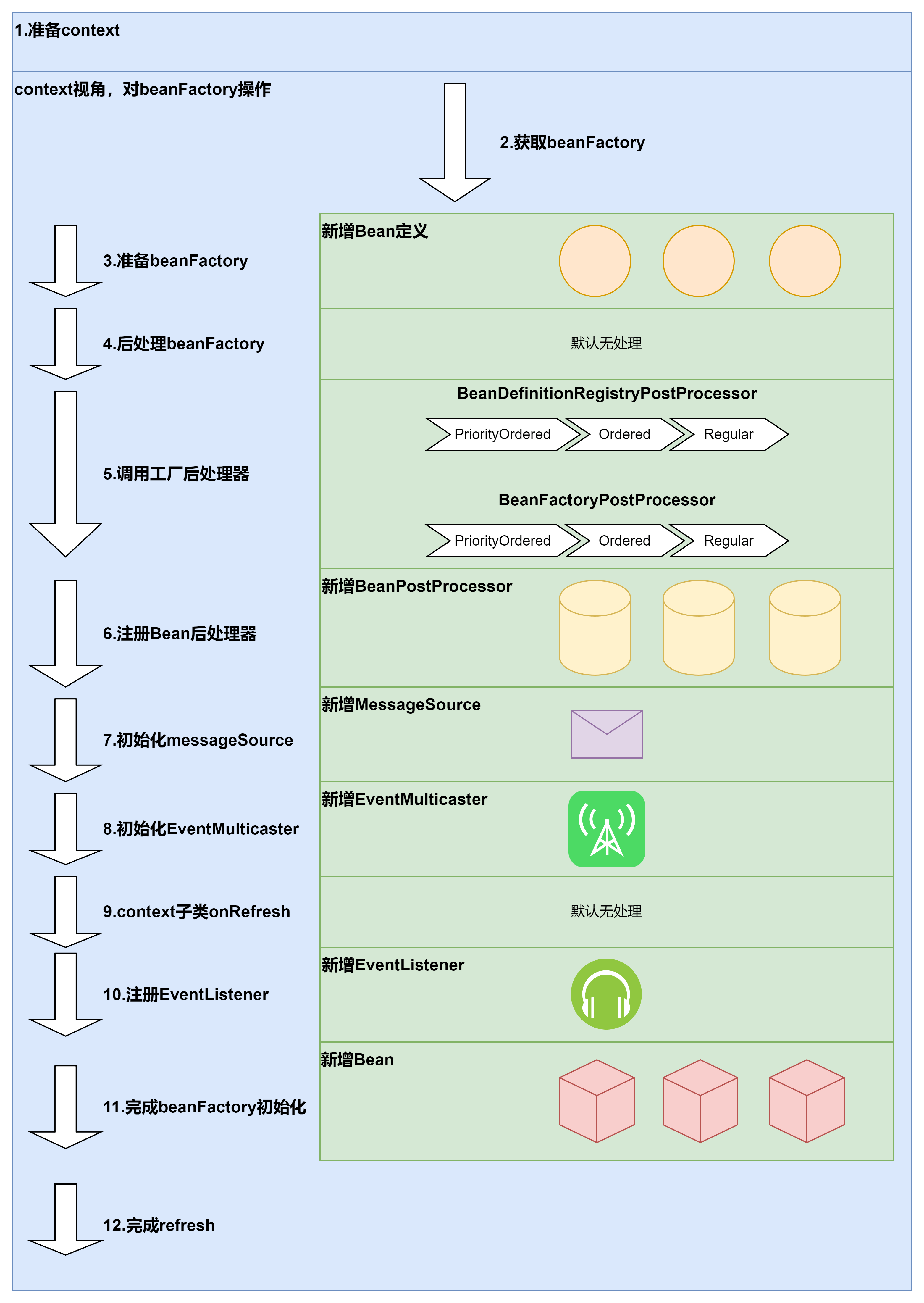
context 刷新流程简单图解 刷新流程 刷新流程中的组件 上下文刷新 AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public void refresh () throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this .startupShutdownMonitor) { prepareRefresh(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); initMessageSource(); initApplicationEventMulticaster(); onRefresh(); registerListeners(); finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { destroyBeans(); cancelRefresh(ex); throw ex; } finally { resetCommonCaches(); } } }
准备 context 以供刷新 prepareRefresh 准备此 context 以供刷新,设置其启动日期和活动标志以及执行属性源的初始化。
编写管理资源的容器时,可以参考。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 protected void prepareRefresh () { this .startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .closed.set(false ); this .active.set(true ); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Refreshing " + this ); } initPropertySources(); getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); this .earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet <ApplicationEvent>(); }
obtainFreshBeanFactory 告诉子类刷新内部 bean 工厂并返回,返回的实例类型为 DefaultListableBeanFactory 。在这里完成了配置文件的读取,初步注册了 bean 定义。
我大概这辈子都不会想理清楚这里面关于 XML 文件的解析过程,但是我知道可以在这里观察到 beanFactory 因为配置文件注册了哪些 bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory () { refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; }
准备 beanFactory 配置 BeanFactory 以供在此 context 中使用,例如 context 的类加载器和一些后处理器,手动注册一些单例。
为 beanFactory 配置 context 相关的资源,如类加载器
添加 Bean 后处理器
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,context 回调,注入特定类型时可触发自定义逻辑
ApplicationListenerDetector,检测 ApplicationListener
手动注册单例
ignoreDependencyInterface 和 registerResolvableDependency 在理解之后比单纯地记忆它们有趣许多。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 protected void prepareBeanFactory (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader()); beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver (beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar (this , getEnvironment())); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor (this )); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this ); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this ); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this ); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector (this )); if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor (beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader (beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment()); } }
在创建 Bean 开始前注册的单例,都属于手动注册的单例 manualSingletonNames
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public void registerSingleton (String beanName, Object singletonObject) throws IllegalStateException { super .registerSingleton(beanName, singletonObject); if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) { synchronized (this .beanDefinitionMap) { if (!this .beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) { Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet <String>(this .manualSingletonNames.size() + 1 ); updatedSingletons.addAll(this .manualSingletonNames); updatedSingletons.add(beanName); this .manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons; } } } else { if (!this .beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) { this .manualSingletonNames.add(beanName); } } clearByTypeCache(); }
postProcessBeanFactory 在标准初始化后修改内部 beanFactory,默认什么都不做。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 实例化并调用所有在 context 中注册的 beanFactory 后处理器,需遵循顺序规则。具体的处理被委托给 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate。
1 2 3 4 protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); }
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法堪比裹脚布。
关于调用顺序的规则 :
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 分为 context 添加的和 beanFactory 注册的,前者优于后者
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 又可分为常规的和 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,后者优于前者
PriorityOrdered 优于 Ordered 优于剩余的
可能新增 beanDefinition 的情况:
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 可能在 beanFactory 中引入新的 beanDefinition
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors ( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet <String>(); if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList <BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList <BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>(); for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>(); String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); boolean reiterate = true ; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false ; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true ; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } else { invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList <String>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList <String>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }
registerBeanPostProcessors 注册拦截 bean 创建的 bean 后处理器。具体的处理被委托给 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate。
1 2 3 protected void registerBeanPostProcessors (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this ); }
registerBeanPostProcessors 相比之下是一条清新的裹脚布。这里特别区分 3 种类型的 Bean 后处理器:
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 感知实例化
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 感知销毁
ApplicationListenerDetector 既是 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor,又是 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor,在初始化后将 listener 加入,在销毁前将 listener 移除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public static void registerBeanPostProcessors ( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true , false ); int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker (beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanPostProcessor>(); List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanPostProcessor>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList <String>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList <String>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector (applicationContext)); }
添加 BeanPostProcessor 时
先移除
再添加
判断类型并记录标记
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public void addBeanPostProcessor (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) { Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null" ); this .beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor); this .beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor); if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { this .hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true ; } if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) { this .hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true ; } }
initMessageSource 初始化消息源。 如果在此 context 中未定义,则使用父级的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 protected void initMessageSource () { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) { this .messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class); if (this .parent != null && this .messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) { HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this .messageSource; if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null ) { hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource()); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using MessageSource [" + this .messageSource + "]" ); } } else { DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource (); dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource()); this .messageSource = dms; beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this .messageSource); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate MessageSource with name '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this .messageSource + "]" ); } } }
initApplicationEventMulticaster 初始化 ApplicationEventMulticaster。 如果上下文中未定义,则使用 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。可以看得出代码的结构和 initMessageSource 是类似的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster () { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { this .applicationEventMulticaster = beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this .applicationEventMulticaster + "]" ); } } else { this .applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (beanFactory); beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this .applicationEventMulticaster); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this .applicationEventMulticaster + "]" ); } } }
onRefresh 可以重写模板方法来添加特定 context 的刷新工作。默认情况下什么都不做。
registerListeners 获取侦听器 bean 并注册。无需初始化即可添加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 protected void registerListeners () { for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); } String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true , false ); for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); } Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this .earlyApplicationEvents; this .earlyApplicationEvents = null ; if (earlyEventsToProcess != null ) { for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); } } }
添加 ApplicationListener。
后处理器 ApplicationListenerDetector 在 processor chain 的最后,最终会将创建的代理添加为监听器。什么情况下会出现代码中预防的情况呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public void addApplicationListener (ApplicationListener<?> listener) { synchronized (this .retrievalMutex) { Object singletonTarget = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(listener); if (singletonTarget instanceof ApplicationListener) { this .defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(singletonTarget); } this .defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener); this .retrieverCache.clear(); } }
finishBeanFactoryInitialization 实例化所有剩余的(非惰性初始化)单例。以 context 视角,是完成内部 beanFactory 的初始化。
几乎可以只关注最后的 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver () { @Override public String resolveStringValue (String strVal) { return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal); } }); } String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false , false ); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { getBean(weaverAwareName); } beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null ); beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
确保所有非惰性初始化单例都已实例化,同时还要考虑 FactoryBeans。 如果需要,通常在工厂设置结束时调用。
加载 Bean 的流程分析在此 。
先对集合进行 Copy 再迭代是很常见的处理方式,可以有效保证迭代时不受原集合影响,也不会影响到原集合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 @Override public void preInstantiateSingletons () throws BeansException { if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this ); } List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList <String>(this .beanDefinitionNames); for (String beanName : beanNames) { RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction <Boolean>() { @Override public Boolean run () { return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit(); } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); } if (isEagerInit) { getBean(beanName); } } else { getBean(beanName); } } } for (String beanName : beanNames) { Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) { final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null ) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction <Object>() { @Override public Object run () { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return null ; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); } } } }
finishRefresh 最后一步,完成 context 刷新,比如发布相应的事件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 protected void finishRefresh () { initLifecycleProcessor(); getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent (this )); LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this ); }